FIACS [FLANDER'S INTERACTION ANALYSIS CATEGORY SYSTEM]
(प्रिय छात्रों जैसा कि आप सभी जानते है कि CTET/UPTET/TET की लिखित परीक्षा समय समय पर आयोजित की जाती हैं
इसी लिए elearnnotes.blogspot.com आप सब छात्रों के लिए सम्पूर्ण UPTET/CTET/TET Study Material Hindi/ENGLISH में लेकर आये है । जिसमें सभी विषयों को नये पैटर्न के आधार पर अध्यायवार विभाजित कर तैयार किया गया है जो कि आप छात्रों के लिए काफी महत्वपूर्ण है। UPTET/CTET/TET/KVS Books in Hindi/English pdf में आपको पर्यावरण, गणित, बाल विकास एवं शिक्षा शास्त्र, हिंदी और अंग्रेजी विषय के लिए अध्ययन सामग्री पढ़नें को मिलेगा। )
According to Daniel G. Bobrow, there are three dimensions of interaction.
1.communication
2. Coordination
3. Integration
Interaction Analysis:
Interaction analysis is a process of encoding and decoding the study pattern of teaching and learning process of classroom.
A typical system for interaction analysis will usually include
According to Dr. S.K. Thakur, classroom interaction analysis may be defined as “an instrument which is designed to record categories of verbal interaction during, or from, recorded teaching learning sessions. It is a technique for capturing qualitative and quantitative dimensions of teacher’s verbal behavior in the classroom.”
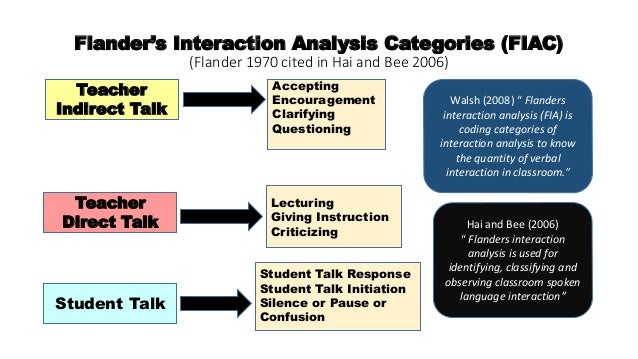
FIACS [FLANDER'S INTERACTION ANALYSIS CATEGORY SYSTEM]
Flanders’ system is an observational tool used to classify the verbal behavior of teachers, and pupils as they interact in the classroom.It was developed by Ned.A Flander used in the year 1959 at University of Minnesota as a teacher training technique.
2.Student talk
3.Silence or confusion
2.Praises or encourages
3.Accepts or uses ideas of pupils
4.Asks questions
5.Lecturing
6.Giving directions
7.Criticising or justifying authority
9. Pupil-talk initiation
1.communication
2. Coordination
3. Integration
Interaction Analysis:
Interaction analysis is a process of encoding and decoding the study pattern of teaching and learning process of classroom.
A typical system for interaction analysis will usually include
- A set of categories, each defined clearly
- A procedure for observation and a set of ground rules
- Steps for tabulating data in order to arrange a display
- Suggestions which can be followed in some of the more common applications
According to Dr. S.K. Thakur, classroom interaction analysis may be defined as “an instrument which is designed to record categories of verbal interaction during, or from, recorded teaching learning sessions. It is a technique for capturing qualitative and quantitative dimensions of teacher’s verbal behavior in the classroom.”
FIACS [FLANDER'S INTERACTION ANALYSIS CATEGORY SYSTEM]
Flanders’ system is an observational tool used to classify the verbal behavior of teachers, and pupils as they interact in the classroom.It was developed by Ned.A Flander used in the year 1959 at University of Minnesota as a teacher training technique.
Basic theoretical assumptions of interaction analysis
- Predominance of verbal communication
- Higher reliability of verbal behaviour
- Consistency of verbal statements
- Teacher’s influence
- Relation between student and teacher
- Relation between social climate and productivity
- Relation between classroom climate and learning
- Use of observational technique
- Role of feedback
- Expression through verbal statement
in Flanders interaction analysis system,the entire classroom interaction is put into three main sections.
1.Teacher talk2.Student talk
3.Silence or confusion
Teacher talk
1.Accepts feeling2.Praises or encourages
3.Accepts or uses ideas of pupils
4.Asks questions
5.Lecturing
6.Giving directions
7.Criticising or justifying authority
Pupil talk
8. Pupil-talk response9. Pupil-talk initiation
Silence
10. Silence or confusionIndirect Influence of Teacher Behaviour Concepts
This is defined as actions taken by the teacher which encourages and support student participation.we can define indirect behaviour operationally by noting the percentage of teacher statements falling into categories 1,2,3,and 4.Direct Influence
This refers to actions taken by the teacher which restrict students participation.This increases the control of the teacher and stimulates conformity and compliance.We can define direct behaviour operationally by noting the percentage of teacher statements falling into categories 5,6,and 7.1.Accepts feeling
Accepts and clarifies an attitude or the feeling tone of a pupil in a non-threatening manner. Feeling may be positive or negative. Predicting and recalling feelings are included.2.Praises or encourages
Praises or encourages pupil action or behavior. Jokes that release tension, but not at the expense of another individual; nodding head, or saying “Um hm?” or “go on” and included3. Accepts or uses ideas of pupils:
Clarifying or building or developing ideas suggested by a pupil. Teacher extensions of pupil ideas are included but as the teacher brings more of his own ideas into play, shift to category five.4.Asking questions
Asking question about content to procedure, based on teacher ideas, with the intent that a pupil will answer.5.Lecturing
Giving facts or opinions about content or procedures; expressing his own ideas, giving his own explanation, or citing an authority other than a pupil.6.Giving directions
Directions, commands or orders to which a pupil is expected to comply .7.Criticizing or Justifing Authority
Statements intended to change pupil behavior from non-acceptable to acceptable pattern; bawling someone out; stating why the teacher is doing what he is during; extreme self-reliance.8.Student talk responses
Talk by pupils in response to teacher. Teacher initiates the contact or solicits pupil statement or structures the situation. Freedom to express own ideas is limited.9.student talk initiations
Talk by pupils, which they initiate. Expressing own ideas; initiating a new topic; freedom to develop opinions and a line of thought, kike asking thoughtful questions; going beyond the existing structure.10.silence or confusion
Pauses, short periods of confusion in which communication cannot be understood by the observer.Procedure of Flander’s Interaction Analysis:
There are two process of interaction anaylsis.
- Encoding process
- Decoding process
The encoding process is used for recording classroom events and preparing observation matrix by encoding the numbers of ten category system.
The decoding is process of interpreting observation matrix.
ENCODING PROCESS
Encoding Process has three steps:
Memorize the code number:The first step in the process of encoding is to memorize the code Numbers, in relation to key phrase of words, which are indicated in capital in ten-category system.
Place of sitting:
An observer sits on the last bench of the classroom and observes the teacher when he is teaching.Recording the category number:
At an interval of every three seconds he writes down that category number which best represents or communication event just completed
for example
- when teacher is lecturing the observer puts 5.
- when he asks question he puts 4.
- when student replies he put 8.
- when teacher praises he puts 2.
- when teacher asks to sit down he puts 6.
- when again the teacher starts lecturing he puts5.
The procedure of recording events goes on at the rate of 20 to 25 observations in per minute
DECODING PROCESS
After encoding the classroom events into ten-category system 10x10 matrix table is prepared for decoding the classroom verbal behavior. The generalized sequence of the pupil-teacher interaction can be estimated in this matrix table. It indicates, what form a pair of categories. The first number in the pair indicates the row and the second number shows the column for example (10-6) pair would be shown by a tally in the cell formed by row 10 and column 6. For example the observer has written down the code numbers beginning with 6 as follows: 6,10,5,1,4,8,8,2,3,6,4,8,9,7.decoding:
*The proportion of teacher talk, pupil talk, and silence or confusion
*The ratio between indirect influence and direct influence
*The ratio between positive reinforcement and negative reinforcement
*Student’s participation ratio
*Steady state cell
*Content cross cell
*Constructive integration cells and vicious cells
INTERPRETATION
TOTAL TEACHER BEHAVIOUR (TTB)
OR
TEACHER TALK(TT):
It represent the performance of a teacher in term sof action reflecting the tendency of teacher talk. It can be concluded as below:
Total of categories 1 to 7
TT= x100
N
Teacher indirect Influence/ Talk
(ITT)/ Area A
It represents the performance of the teacher in terms of his action encouraging and supporting student’s participation:
Total of categories 1 to 4
ITT= x100
N
Pupil Talk (PT)/ Area C
It concerns pupils’ verbal activities in response to the teacher:
Total of categories 8 to 9
DTT= x100
N
Silence or confusion (SC)/ Area D
It represent silence during teaching which may be due to confusion or any other reason
Total of category 10
SC= x100
N
Indirect to Direct Teacher Talk Ratio(ID Ration)
It represent the proportion of indirect to direct influence:
Total of categories 1to 4
I/D= x100
Total of categories 5 to 7
Pure Indirect to Pure Direct Influence Ratio(ID Ration)
It represent the proportion of pure indirect to pure direct influence:
Total of categories 1,2 to 3
I/D= x100
Total of categories 6 to 7
Pupil initiation Ratio(PIR)
It represent the pupil talk judged by the observer to be an act of initiation:
Total of category9
PIR= x100
Total of categories 8 to 9
Teacher Response Ratio(TRR)
It represent an index of teacher’s tendency to react to the ideas and feeling of students:
Total of categories 1,2 and 3
TRR= x100
Total of categories 1,2,3,6 to 7
Content Cross Ratio(CCR)
It represents the proportion of class room activities related to the teacher’s questions and lecturing with total contents:
Total of category 4 and 5
CCR= x100
N
Advantages
Dr. M.B. Buch says, it is “ a bold step in the right direction to improve the quality of education.”
Feedback to the teacher
Observation technique for classroom behaviour
Useful for theory of teaching
Effective diagnostic tool to measure the social-emotional climate in the classroom
It supplements the training techniques like microteaching and team teaching
Limitations
1. The system does not describe the totality of the classroom activity. Some behavior is always over looked and who is to say that the unrecorded aspects of the teaching act are more important than those recorded.
2. Efforts to describe teaching are often interpreted as evaluation of the teaching act and of the teacher. While descriptions may be used as a basis of evaluation, judgment can be made only after additional value assumptions are identified and applied to the data.
3. The system of interaction analysis is content-free. It is concerned primarily, with social skills of classroom management as expressed through verbal communication.
4. It is costly and cumbersome and requires some form of automation in collecting and analyzing the raw data. It is not a finished research tool.
5. Much of the inferential power of this system of interaction analysis comes from tabulating the data as sequence pairs in a 10 x 10 matrix. This is a time consuming process.
6. Once the high cost of tedious tabulation (electric computers) is under control but the problem of training reliable observers and maintaining their reliability will still remain.
7. Its potential as a research tool for a wide application to problems is to be explored.
The system devotes little attention to student talk and focuses a great deal of attention on direct/ indirect nature of Teachers performance. It is considered a great drawback of Flanders system.
Mathematics-I Notes : Matrices
1. परिभाषा (Definition)
mn संख्याओं (वास्तविक अथवा काल्पनिक) को m पंक्तियों तथा n स्तम्भों में व्यवस्थित करने पर जो आयताकार सारणी (Rectangular Array) प्राप्त होती है, उसे m×n आव्यूह कहते हैं|
अथवा
m n संख्याओं के ऐसे समुच्चय को जो m पंक्तियों तथा n स्तम्भों वाली आयताकार सारणी के रूप में व्यवस्थित होता है, m×n आव्यूह (m by n Matrix) कहते हैं|
याद रखिए (note):
आव्यूह आयताकार सारणी के रूप में व्यवस्थित कुछ संख्याओं का एक समुच्चय मात्र है|
आव्यूह का कोई संख्यात्मक मान नही होता है|
* आव्यूह के अवयव (Elements of a Matrix):
कोई आव्यूह जिन संख्याओं से निर्मित होता है, उन्हें उस आव्यूह के अवयव कहते हैं|
I. आव्यूह के अवयवों को कोष्ठक के अन्दर लिखा जाता है|

I. आव्यूह का क्रम लिखते समय पहले सदैव पंक्तियों की संख्या तथा इसके बाद स्तम्भों की संख्या लिखी जाती है|
II. यदि किसी आव्यूह का क्रम है तो उस आव्यूह में पंक्तियों की संख्या = m तथा स्तम्भों की संख्या = n.
III. आव्यूह में पंक्तियों तथा स्तम्भों की संख्या बराबर होना आवश्यक नहीं है|
IV. आव्यूह किसी आव्यूह में m पंक्तियों तथा n स्तम्भ है तो उस आव्यूह में अवयवो की संख्या = पंक्तियों की संख्या × स्तम्भों की संख्या = mn
2. आव्यूह का निरूपण (Representation of a Matrix)
आव्यूह को प्राय: अंग्रेज़ी वर्णमाला के बड़े अक्षरों A,B,C…….से तथा इनके संगत छोटे अक्षरों के साथ द्वि-अनुलग्न लगाकर आव्यूह के अवयवों को निरुपित किया जाता है जबकि द्वि-अनुलग्न (Double Suffix) का पहला अंक सदैव उस पंक्ति की संख्या को एवं दूसरा अंक सदैव उस स्तम्भ की संख्या को व्यक्त करता है जिसमें अवयव है|







अदिश आव्यूह (Scalar Matrix) : ऐसा विकर्ण आव्यूह जिसके सभी विकर्ण तत्व समान होते हैं| अदिश आव्यूह कहलाता है|
अथवा
ऐसा वर्ग आव्यूह जिसके विकर्ण के सभी अवयव समान तथा शेष सभी अवयव शून्य होते हैं, अदिश आव्यूह कहलाता है|

याद रखिए (Note) :
1. प्रत्येक इकाई आव्यूह एक अदिश आव्यूह होता है|
2. प्रत्येक अदिश आव्यूह एक विकर्ण आव्यूह होता है|
उपरित्रिभुजीय आव्यूह (Upper Triangular Matrix) :
ऐसा वर्ग आव्यूह जिसके मुख्य विकर्ण के नीचे सभी अवयव शून्य होते हैं, उपरित्रिभुजीय आव्यूह कहलाता है|

निम्न त्रिभुजीय आव्यूह (lower triangle matrix) :
ऐसा वर्ग आव्यूह जिसके मुख्य विकर्ण के ऊपर सभी अवयव शून्य होते हैं, निम्न त्रिभुजीय आव्यूह कहलाता है|

(3). A में पंक्तियों की संख्या = B में पंक्तियों की संख्या
अर्थात m = r
(4). A में स्तम्भों की संख्या = B में स्तम्भों की संख्या
अर्थात n = s

5. अव्युहों का योग (Addition of matrices) :
यदि A और B समान क्रम के दो आव्यूह हैं तो इनका योगफल (A+B) उसी क्रम का एक ऐसा आव्यूह होता है जो A तथा B के संगत अवयवों को जोड़ने पर प्राप्त होता है|
उदाहरण :

OTHER LINK FOR DOWNLOAD :-
English For General Competition From Plinth To Paramount (सभी परीक्षाओ के लिए बेहतरीन )
दोस्तों अगर आपको किसी भी प्रकार का सवाल है या ebook की आपको आवश्यकता है तो आप निचे comment कर सकते है. आपको किसी परीक्षा की जानकारी चाहिए या किसी भी प्रकार का हेल्प चाहिए तो आप comment कर सकते है. हमारा post अगर आपको पसंद आया हो तो अपने दोस्तों के साथ share करे और उनकी सहायता करे. आप हमसे Social Groups से भी जुड़ सकते है Daily updates के लिए.
THANKS
TEAM:- ELEARN
THANKS
TEAM:- ELEARN














0 Comments